book reviews
Love and Technology: An Ethnography of Dating App Users in Berlin – review
Fabian Broeker‘s Love and Technology: An Ethnography of Dating App Users in Berlin explores how dating apps mediate intimacy among young Berliners. Presenting an immersive ethnography of app usage, users’ experiences and perceptions and Berlin’s particular dating culture, Jiangyi Hong finds the book a rich work of contemporary digital anthropology.
Love and Technology: An Ethnography of Dating App Users in Berlin. Fabian Broeker. Routledge. 2023.
 With the advent of digital communications technology, dating apps have provided new avenues for finding and nurturing romantic relationships, while also raising many critical questions for social scientists. A recent concern in digital anthropology is that of social relationships and interaction patterns. Intimacy, which people desire in their primary relationships, is now often mediated by dating apps that intervene in one’s lived experience. Fabian Broeker’s Love and Technology: An Ethnography of Dating App Users in Berlin is an immersive ethnography exploring the mediation of intimacy in personal relationships in Berlin.
With the advent of digital communications technology, dating apps have provided new avenues for finding and nurturing romantic relationships, while also raising many critical questions for social scientists. A recent concern in digital anthropology is that of social relationships and interaction patterns. Intimacy, which people desire in their primary relationships, is now often mediated by dating apps that intervene in one’s lived experience. Fabian Broeker’s Love and Technology: An Ethnography of Dating App Users in Berlin is an immersive ethnography exploring the mediation of intimacy in personal relationships in Berlin.
Through a combination of digital ethnography and narrative methods, Broeker provides an in-depth exploration of the romantic lives of young, Berlin-based dating app users. The ethnographic research entailed online and offline participant observation of how young people in Berlin use dating apps and how the apps shape the experiences, behaviours and perceptions of individuals seeking romantic relationships, sexual experiences and love.
Broeker is primarily concerned with Tinder, Bumble, and OkCupid, the three most popular apps encountered in the fieldwork, and describes different dating experiences, finding that young people in Berlin often use more than one app. Throughout this study, Broeker mentions the notion of “affordances” (1), which occur when particular actions and social practices are made easier or preferable due to “a specific cultural context and setting” (2). Broeker foregrounds the affordances dating apps allow without neglecting the fluid relationship between the user, social and material environment, and technological artefacts.
‘Each app on a phone act[s] as a certain canvas of projection’ (25) that shapes and is interpreted based on young dating users’ own experiences, social circles, and cultural values.
In his fieldwork, Broeker explored what each dating app means to participants, the experiences each app could enable, and the coded notion of intimacy in each app (eg, Tinder is associated with primarily brief sexual encounters). Broeker unfolds the complex relationship between users and dating apps, paying particular attention to how “each app on a phone act[s] as a certain canvas of projection” (25) that shapes and is interpreted based on young dating users’ own experiences, social circles, and cultural values. Positioning dating app users alongside this understanding of intimacy, Broeker astutely observes that for these users, switching between different dating apps is not only about browsing their availability to chat with potential partners but also “symbolises about their own identity and the community their membership would align them with” (37).
As Broeker discusses, in the context of this affordance environment, it is worth considering how other forms of mediated communication affect the dating rituals of Berlin’s dating app users. Therefore, he acknowledges in the field survey the importance “within dating rituals of moving from dating apps to other communication services within the framework of users’ mobile devices and the particular social and technological implications of such transitions” (50). Using the term “ritual”, Broeker tends to view dating as an activity that entails multiple actions within underlying meanings and emphases, some being pivotal moments in the development of the relationship and intimacy. Broeker’s work continues along that trajectory, showing not only how the recognition of the courtship rituals inherent in the dating app affects young people in Berlin, but also the significance of traditionally gendered heterosexual dating rituals, (eg, men taking the initiative in dating).
One area where Broeker succeeds is his nuanced discussion of awareness of social manipulation of space (eg, date locations) and personal understandings of intimacy among dating app users in Berlin.
As Broeker contends, the city space is an important arena in which people use dating apps. That space is formed of social relations and carries a plethora of nuanced social cues and rituals. Broeker spent a lot of his time going to different participants’ workplaces or residences and completed interviews with participants in different streets and neighbourhoods. One area where Broeker succeeds is his nuanced discussion of awareness of social manipulation of space (eg, date locations) and personal understandings of intimacy among dating app users in Berlin. This is significant because previous studies about users’ dating experiences often overlooked multiple interpretations of how people move in and choose to occupy cities. This book speaks directly to that aspect – for example, the perception of a user’s choice for a date location will affect people’s first dating impression; different places integrated into the self-presentation of impression management when people design their profiles; and the choice of the location of the first meeting is regarded as reflecting their personality. Therefore, as Broeker explains, city space is positioned as a stamp of dating users’ identity. How to interpret identity and project their values and desires into city space has become a key moment for users to consider on dating apps.
The dating culture of Berlin is included in the idea of an ‘anything is possible’ city hosting limitless hedonistic possibilities.
Berlin is not only a series of spaces but also an area for dating app users to explore and navigate, and it “is built upon a collective imagination” (133). Broeker interprets participants’ conversations and personal descriptions of the dating experience to show that the city is “a particularly free, inclusive and open metropolis”, giving Berlin “the reputation of a particularly free hedonistic paradise” (133). Therefore, the dating culture of Berlin is included in the idea of an “anything is possible” city hosting limitless hedonistic possibilities.
Another important contribution Broeker makes is his analysis of Berlin’s particular dating culture, with a broader understanding of the intimate relationships that the city’s youth form through dating apps. Broeker discusses Berlin’s unique dating culture through two practices, “stories” (119) and “screenshots” (123). Stories are a form of social currency in people’s social activities, traded in conversation. People share their dating experiences by talking with others and trying to narrate unique dating stories, a common topic in their social circles. Broeker suggests that some people even want to have bad experiences to attract others.
Broeker argues that while the app expands the interaction of potential partners, the use of apps limits the narrative of intimate relationships, making encounters less romantic and special.
Screenshots also play a role in dating experiences. Broeker points out that sharing screenshots is not only a central means by which dating users in Berlin communicate their dating experiences, but also a tool for Berlin young people to “see” dates through visual or textual images on communication platforms. This exploration of storytelling and screenshots circles back to a discussion of dating culture in Berlin. Broeker notes that although the dating app provides a tangible nucleus for users around which dating stories can be constructed and explored, respondents still focused on the idea of nostalgic romantic narratives. Thus, he argues that while the app expands the interaction of potential partners, the use of apps limits the narrative of intimate relationships, making encounters less romantic and special.
While the book’s in-depth presentation and excellent analysis of ethnographic details and theory are impressive, some readers may find its academic nature and use of technical terms difficult. Broeker’s assumption of some knowledge of academic discourse (such as the assumed knowledge of rituals of intimacy and academic definition of polymedia) may be off-putting and inaccessible for the general reader. Overall, Love and Technology is an intelligent and perceptive contribution to the field of digital anthropology. Readers can gain important insights into the intricate interplay between technology, culture and intimacy from Broeker’s work. This book will inspire and provoke thought, regardless of whether you are a scholar interested in modern intimacy and its relations to technology or a general reader interested in the ways that technology impacts our romantic lives.
Note: This post gives the views of the author, and not the position of the LSE Review of Books blog, or of the London School of Economics and Political Science.
Image credit: Studio Romantic on Shutterstock.
Industrial Policy in Turkey: Rise, Retreat and Return – review
In Industrial Policy in Turkey: Rise, Retreat and Return, Mina Toksoz, Mustafa Kutlay and William Hale analyse Turkey’s industrial policy over the past century, highlighting the interplay of global paradigms, macroeconomic stability and domestic institutional contexts. The book offers a timely analyses of industrial policy’s past and possible future trajectories, though it stops short of interrogating exactly how cultural, social, political and economic factors shape state-business relations and bureaucracy, writes M Kerem Coban.
Industrial Policy in Turkey: Rise, Retreat and Return. Edinburgh University Press. 2023.
 Is industrial policy back? The Biden administration’s Inflation Reduction Act and the CHIPS and Science Act, or the 2016 UK industrial policy are only two contemporary examples. These policies seek to address value chain bottlenecks, as well as the question of how to “take back control” in manufacturing and key sectors, along with concerns about gaining or sustaining economic edge and autonomy
Is industrial policy back? The Biden administration’s Inflation Reduction Act and the CHIPS and Science Act, or the 2016 UK industrial policy are only two contemporary examples. These policies seek to address value chain bottlenecks, as well as the question of how to “take back control” in manufacturing and key sectors, along with concerns about gaining or sustaining economic edge and autonomy
In this context, the Turkish experience is illustrative for making sense of the trajectory of industrial policy in a major developing country. Mina Toksoz, Mustafa Kutlay and William Hale examine the evolution of industrial policy in Turkey. They present an accessible, detailed account of the trajectory and evolution of the policy since the establishment of the Republic, which argues that we had better study “the conditions under which state intervention works, rather than whether the state should intervene in the economy” (26, emphasis in original).
[The authors] suggest that effective industrial policy is the outcome of the interaction between global development policy paradigms, macroeconomic (in)stability, and the domestic institutional context.
The book is divided into five chapters. Chapter One discusses the political economy of industrial policy and sets out an analytical framework. The authors assert that analyses should go beyond dichotomies (eg, horizontal vs. vertical policies; export-led vs. import-substituting industrialisation) and that a broader understanding requires identifying the factors and conditions of effective industrial policy. They suggest that effective industrial policy is the outcome of the interaction between global development policy paradigms, macroeconomic (in)stability, and the domestic institutional context. Global development policy paradigms evolved from étatism of the 1930s, import-substituting industrialisation in the 1960s and the 1970s, neoliberalism of the 1980s, and the return of industrial policy after the 2008 Financial Crisis. Macroeconomic (in)stability drives (un)certainty regarding economic policies and instruments and the trajectory of economy, which, in turn, regulates investment decisions. Finally, the domestic institutional context concerns how state-society, or state-business, relations are structured, whether the state capacity is sufficient to resolve conflicts, discipline and coordinate actor behaviour, and whether bureaucracy has capabilities to formulate and implement policies. Figure 1 seeks to summarise the main argument of the book.
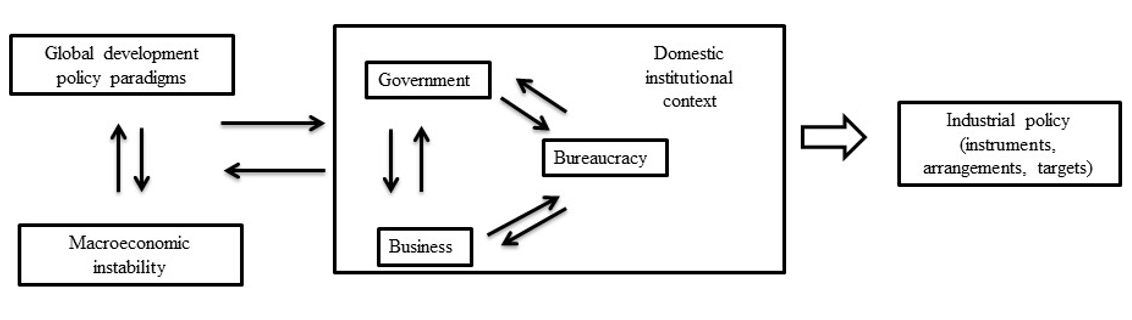 Figure 1: Flow chart summarising the book’s main argument. Source: M Kerem Coban.
Figure 1: Flow chart summarising the book’s main argument. Source: M Kerem Coban.
Chapter Two focuses on the longue durée between 1923 and 1980. From the ashes of incessant wars that ruined the already unsophisticated infrastructure and demographic challenge, the new Republic had to build a new nation. Yet the rise of the state interventionist era in the 1930s drove policymakers towards the first industrialisation plan and the opening of many industrial sites across the country. When the Democrat Party assumed power, the interventionist, planning-based industrial policy was scrutinised for liberalisation that even included state-owned enterprises to be released to set up their own prices (73).
At the same time, business was encouraged to invest. For example, the fruits of these included Otosan or BOSSA (75). Between 1960 and 1980, the authors underline the second planning period with the establishment of the State Planning Organisation (SPO). SPO boosted bureaucratic and planning capacity and capabilities for disciplined, systematic industrial policy during the era of import-substitution.
Between 1980 and 2000 […] Turkey shifted to export-led growth and liberalised trade and financial flows. These shifts had profound implications for bureaucracy
The third chapter examines demoted industrial policy between 1980 and 2000 when Turkey shifted to export-led growth and liberalised trade and financial flows. These shifts had profound implications for bureaucracy: SPO was sidelined, parallel bureaucratic networks of Ozal were implanted with the opening of new offices or agencies. Consequently, the role of state became less coherent, as political uncertainty driven by unstable coalitions eroded the market-shaping role of the state. The financial sector did not help industrial policy, since banks were dominantly financing chronic budget deficits during a period of high inflation (111). What is more, business, including Islamic conservative SMEs in Anatolia, reduced or ignored investments in manufacturing given the clientelist state-business relations that incentivised construction, real-estate development (115), emphasis in original). Finally, the external conditions were not disciplinary: accession to the Customs Union with the European Union and the World Trade Organization ruled out export support and import restricting measures, among other trade regulatory instruments.
The fourth chapter claims that industrial policy retreated between 2001 and 2009. The first years of this period was marked by political instability and a local systemic banking crisis and its resolution, and Justice and Development Party (AKP in Turkish) assumed power. During this period, industrial policy was dominated by institutionalisation of the regulatory state and the privatisation of state-owned enterprises, the establishment of autonomous regulatory agencies and are structured banking sector. While the regulatory capacity of the state increased, privatisation and the regulation of the market were highly politicised. For example, “a major cycle of gas privatisation saw ‘politically connected persons’ winning fifteen out of nineteen metropolitan centres and serving 76 percent of the population” (161). In such a politically compromised setting, which was accompanied by the institutionalisation of the capital inflow-dependent credit-led growth model that prioritised “rent-thick” sectors, industrial policy could not flourish.
While the regulatory capacity of the state increased, privatisation and the regulation of the market were highly politicised.
The fifth chapter locates the policy within the global ideational and political economic context that marks the return of industrial policy in various forms. In line with policy documents such as the 11th Development Plan, horizontal measures, private and public R&D spending on high-tech initiatives, electric vehicle manufacturing attempt, and most notably the advancements in defence sector have constituted the revival of industrial policy. At the same time, the authors point to several challenges such as eroded academic research and quality and a lack of investment in ICT skills. Additionally, R&D subsidies or other industrial policy measures require thorough performance criteria and measurement to discipline actor behaviour and regulate the incentive structures.
Industrial Policy in Turkey is a timely contribution to the current debate. Its historical account and analysis of current policies, instruments, and the potential trajectory of industrial policy are its main strengths. Still, there are several caveats. First, the book’s framework is not systematic, which causes some confusion. For example, the book does not demonstrate a convincing link between the role and impact of autonomous agencies on industrial policy. Second, the book leaves the reader with more questions than answers, one of which relates to the effect of bureaucratic fragmentation in shaping industrial policy. Another is around the implications of state-business for bureaucracy, and consequently, industrial policy.
The book leaves the reader with more questions than answers, one of which relates to the effect of bureaucratic fragmentation in shaping industrial policy.
Third, the trajectory of industrial policy cannot be considered independently from the shifts in growth models. Yet the fact these shifts occur because the country depends on hard currency earnings for capital accumulation and to finance consumption and investments: Turkey either relies on capital flows or export earnings, in addition to tourism and (un)recorded (illicit) flows. Pendulums between these channels imply that the country cannot design and implement disciplined, systematic industrial policy. Put differently, there are macroeconomic and financial structural impediments against generating hard currency earnings. Industrial policy is one of the remedies, however, the macroeconomic and structural transformative consequences of the latest episode of emphasis on industrial policy and the export-driven growth experiment in Turkey are yet to be seen.
Finally, and perhaps most importantly, the book tends to relegate a core problem of coordination, long-term policy design and implementation to “governance issues”. Deeper cultural, social, political and economic factors determine the clientelist state-business relations and their effect on bureaucracy and bureaucratic autonomy. Such deeper ties have been masked by instrumentalised “democratisation reforms” or higher economic growth rates in the previous years. In this context, is the more critical problem the purposefully immobilised or challenged infrastructural power to coordinate societal actors? If that is true, then should we make interdisciplinary attempts to identify this problem’s core determinants?
Note: This interview gives the views of the author, and not the position of the LSE Review of Books blog, or of the London School of Economics and Political Science.
Image credit: Chongsiri Chaitongngam on Shutterstock.
On Book Reviews
There has been discussion among some philosophers on social media about the decline in the number of book reviews published by Notre Dame Philosophical Reviews (NDPR).

[detail of “Pile of Books” by Cornelius Volker]
Last year NDPR published 65 book reviews. But in the years 2006-2019 the number of reviews published there annually ranged from 250 to 426.
Of course, NDPR isn’t the only outlet for reviews of philosophy books. Many journals publish book reviews.
Last year, in attempt to provide a central hub for the listing of these book reviews, and greater publicity for them, Daily Nous started including in its Online Philosophy Resources Weekly Updates book reviews published in journals, provided they were open access.
Responsibility is with the journals to let us know when new open access reviews are published, however, and only a small number of journals do so regularly.
If more journals made their book reviews open access, and more journals regularly sent in to us their open access book reviews for inclusion in the Weekly Updates, that might go some of the ways to making up for the slowdown at NDPR. Journal editors, please consider doing both of these things, if possible. Thanks.
The post On Book Reviews first appeared on Daily Nous.
Online Philosophy Resources Weekly Update
The weekly report on new and revised entries at online philosophy resources and new reviews of philosophy books…

Reminder: if your journal publishes open-access book reviews, please send in links to them for inclusion in future weekly updates.
New:
- Moral Decision-Making Under Uncertainty by Christian Tarsney, Teruji Thomas, and William MacAskill.
- Aesthetic Testimony by Jon Robson and Rebecca Wallbank.
Revised:
- Herbert Spencer by David Weinstein.
- Epistemology in Classical Indian Philosophy by Stephen Phillips and Anand Vaidya.
- Darwin: From the Origin of Species to the Descent of Man by Phillip Sloan.
- Giordano Bruno by Dilwyn Knox.
IEP ∅
NDPR ∅
- Hegel’s Ontology of Power: The Structure of Social Domination in Capitalism by Arash Abazari is reviewed by Shahriar Khosravi.
- The Readability of the World by Hans Blumenberg, (R. Savage & D. Roberts, Trans.), is reviewed by Evan Kuehn.
- Pre-Liberal Political Philosophy: Rawls and Plato, Aristotle, Augustine, Aquinas by Daniel A. Dombrowski is reviewed by Travis Hreno.
- Mandeville’s Fable: Pride, Hypocrisy, and Sociability by Robin Douglass is reviewed by Elad Carmel
- Materialism from Hobbes to Locke by Stewart Duncan is reviewed by Geoffrey Gorham
- A Certain Gesture: Evnine’s Meme Project and its Parerga! Volume 1 by Simon J. Evnine (Ed.) is reviewed by Nicholas Wiltsher.
- Why Teach Philosophy in Schools? by Jane Gatley is reviewed by Robert Hudson.
- Introducing Philosophy through Pop Culture: From Socrates to Star Wars and Beyond by William Irwin and David Kyle Johnson, eds. is reviewed by Mark Porrovecchio.
- Theories of Consciousness and the Problem of Evil in the History of Ideas by Ben Lazare Mijuskovic is reviewed by Michael D. Bobo.
- The Life and Thought of H. Odera Oruka: Pursuing Justice in Africa by Gail M. Presby is reviewed by Zeyad El Nabolsy.
- Having Too Much: Philosophical Essays on Limitarianism by Ingrid Robeyns is reviewed by Aaron Landry.
- The Failure of Philosophical Knowledge: Why Philosophers are not Entitled to their Beliefs by János Tőzsér is reviewed by Aron Dombrovszki.
- Interpreting Cassirer: Critical Essays by Simon Truwant is reviewed by Giacomo Borbone.
- Identifying Future-Proof Science by Peter Vickers is reviewed by Glenn Branch.
- Magnificent Rebels: The First Romantics and the Invention of the Self by Andrea Wulf & Time of the Magicians: The Invention of Modern Thought, 1919-1929 by Wolfram Eilenberger are reviewed by Richard Nigel Mullender.
- The Function of Biochemical Functions: What does it mean to say a biochemical has a function? by Francesca Bellazzi.
Open-Access Book Reviews in Academic Philosophy Journals
- Conjunctive Explanations by Jonah N. Schupbach and David H Glass is reviewed by Naftali Weinberger at The British Society for Philosophy of Science.
Recent Philosophy Book Reviews in Non-Academic Media
- On Gaslighting by Kate Abramson is reviewed by Dodai Stewart at The New York Times.
- Spinoza: Life and Legacy by Jonathan I. Israel is reviewed by Carlos Fraenkel at The Times Literary Supplement.
- Who’s Afraid of Gender by Judith Butler is reviewed Lyndsey Stonebridge at The New Statesman and by Jane O’Grady at The Telegraph.
Compiled by Michael Glawson
BONUS: If virtue is its own reward, and people should get what they deserve, then…
The post Online Philosophy Resources Weekly Update first appeared on Daily Nous.
Tactical Publishing: Using Senses, Software, and Archives in the Twenty-First Century – review
In Tactical Publishing: Using Senses, Software, and Archives in the Twenty-First Century, Alessandro Ludovico assembles a vast repertoire of post-digital publications to make the case for their importance in shaping and proposing alternative directions for the current computational media landscape. Although tilting towards example over practical theory, Tactical Publishing is an inspiring resource for all … Continued
Rethinking Drug Laws: Theory, History, Politics – review
In Rethinking Drug Laws: Theory, History, Politics, Toby Seddon analyses drug control policy and argues for a paradigm shift that decentres the West and recognises China’s historical and contemporary influence. Unpacking the complexity of drug law as a regulatory system, Seddon’s well-argued, insightful book calls for more inclusive, evidence-informed and democratic policymaking, writes Mark Monaghan.
Rethinking Drug Laws: Theory, History, Politics. Toby Seddon. Oxford University Press. 2023.
 Based on forensic archival research, Rethinking Drug Laws: Theory, History, Politics by Toby Seddon is beautifully written and deeply insightful. Its central thesis is that we must decentre the West, especially when thinking about the origins of drug policy. Viewing drug policy from a Western vantage point is a blip because, as Seddon shows, China has long been a key player on the global stage, but drug policy analysis, with some exceptions, has not always recognised this. In this way, drug policy analysis has fallen into the trap of Occidentalism, providing a distorted view of the West’s prominence. Seddon sets out to show the folly of this and succeeds. Furthermore, he demonstrates that there are signs of regression toward the mean as China once again is becoming a primary global player, particularly through the belt and road initiative.
Based on forensic archival research, Rethinking Drug Laws: Theory, History, Politics by Toby Seddon is beautifully written and deeply insightful. Its central thesis is that we must decentre the West, especially when thinking about the origins of drug policy. Viewing drug policy from a Western vantage point is a blip because, as Seddon shows, China has long been a key player on the global stage, but drug policy analysis, with some exceptions, has not always recognised this. In this way, drug policy analysis has fallen into the trap of Occidentalism, providing a distorted view of the West’s prominence. Seddon sets out to show the folly of this and succeeds. Furthermore, he demonstrates that there are signs of regression toward the mean as China once again is becoming a primary global player, particularly through the belt and road initiative.
In drug control, inanimate objects – drugs – are not banned, but transactions that would otherwise constitute lawful economic activity are criminalised.
A defining feature of Seddon’s writing is the remarkable capacity for distilling complex historical narratives into an easily digestible schema. We see this clearly in the introduction, where he proposes a tripartite structure of race, risk and security arcs as ways to think about the origins of what has only recently become known as the “drug problem”. We are also introduced to another key idea that drug laws function through controlling the circulation of goods, ie, they are regulatory systems. In drug control, inanimate objects – drugs – are not banned, but transactions that would otherwise constitute lawful economic activity are criminalised. This is about the control of personal property rights. The right to personal property is not explicitly eroded through prohibition, but some transactions in relation to them become impermissible and there is no legal recourse for the right to conduct these transactions. In outlining this, the entire premise of drug control shifts from one of a struggle between the forces of prohibition and legalisation to understanding legalisation and prohibition within a broader system of regulation.
Seddon refers to regulatory systems as ‘exchangespace’. […] The basic premise of exchangespace is that ‘market behaviour and regulation are not separate realms but two sides of the same coin’.
Seddon elaborates on this over the following chapters and in doing so demonstrates a depth of research and scholarship that is genuinely cross-disciplinary, bringing in economics, sociology, history, political economy as well as insights from criminology, regulation theory and socio-legal perspectives. There is, however, method to this, which shapes and is shaped by the development of a new conceptual framework. Drawing on the work of Clifford Shearing and others, Seddon refers to regulatory systems as “exchangespace”, and this is painstakingly outlined in Chapter Two. The basic premise of exchangespace is that “market behaviour and regulation are not separate realms but two sides of the same coin”. The dimensions of exchangespace can be summarised as:
- Regulation operates in networks consisting of multiple dimensions and participants.
- Nodes are a key element of networks and facilitate communication across them. Analysis of networks should, therefore, look at the nodes because these are the locus within a system where various resources are mobilised in order to govern effectively.
- Not all nodes exert the same amount or kind of power in the network. The most economically powerful nodes can distort the smooth operation of the entire system.
- Networks adapt overtime. Consequently, policy does not stand still, it evolves and emerges in often unpredictable ways.
Seddon encourages us to focus on the network conditions that led to increasing control of certain substances (what we know as drugs), whilst permitting or at least freeing the trade in others (coffee, alcohol and tobacco) and to view these as complex systems.
Seddon encourages us to focus on the network conditions that led to increasing control of certain substances (what we know as drugs), whilst permitting or at least freeing the trade in others (coffee, alcohol and tobacco) and to view these as complex systems. In complex systems, the outcomes of policy depend on understanding where the starting point is. However, identifying starting points is almost impossible, not least, as Seddon contends, because we don’t yet have the theory and methods at our disposal to do so. The best we can do, then, is to try and understand elements of the wider network; that is, which nodes are exerting power in which contexts while acknowledging that these systems are unpredictable and constantly changing. Seddon uses this framework to explain the origins of Cannabis Social Clubs in Catalonia and the complex politics behind the patchy implementation of Heroin Assisted Treatment. In this way, we can start to explain the ways in which, for example, overdose prevention centres have been established in some locations and not others, or why and how drugs were decriminalised in Oregon, a decision that may now be reversed.
Seddon demonstrates how the origins of the current system can be traced to colonialism […] in the nineteenth century, even if we cannot pinpoint the exact starting point.
A complex system like drug policy can never revert to an earlier stage of development. Oregon’s post-decriminalisation society will not be the same as its pre-decriminalisation society. Fortunately, however, complex systems do have path dependency, and so it is possible, as Seddon does in Part II (Chapters Four and Five), to outline the chain of events that has led to the contemporary global drug regulatory system. Seddon demonstrates how the origins of the current system can be traced to colonialism (the race arc) in the nineteenth century, even if we cannot pinpoint the exact starting point. The key lesson here is that we need to look East rather than West to understand this. Here, the Opium Wars of the nineteenth century are a key reference point.
Taking an exchangespace perspective we see that the Opium Wars (1839-1842) were more than just about one country (Britain) establishing a right to export its products (opium) to a large market (China). More accurately, they represented a military contestation that focused on the boundaries between legal and illegal trade – a contestation that lies at the heart of drug control. The burgeoning temperance movement proved a powerful node alongside increasingly powerful US economic interests, which contributed to the realigning of opium in the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries as a product requiring control. The Opium Wars also represent – in the form of the second opium (Arrow) war – the first moment that drug control (as opium control) became a multinational affair. In this way we can draw a direct line from the Opium Wars to global drug prohibition fifty years later.
In Part III (Chapters Six and Seven) Seddon turns to the political nodes of the regulatory network, focusing on “what is at stake when drug laws and drug policy become a matter of political contestation”. The idea here is that within exchangespace, it is impossible to stand outside of politics, as the system is inherently political. Politics is a powerful node. This section draws heavily on Loader and Sparks’ conception of public criminology and the strategies that can be used to add coolant to heated debates.
To hand over decision making to experts is to abandon any hope for democratic politics as it replaces one system of domination (populist politics) with another (experts).
For Seddon, this should not simply mean that populist ideas – such as the “war on drugs” – are replaced with technocratic, evidence-based decisions. To hand over decision making to experts is to abandon any hope for democratic politics as it replaces one system of domination (populist politics) with another (experts). Arguably, that is why it has become more commonplace to speak of evidence-informed or evidence-inspired policy. However, Seddon provides a way out of that impasse by stating that “better politics” is required more than better evidence. This has two dimensions. First, we need a more careful analysis that focuses not only on the impact or harms of current drug policies (eg, criminalisation, stigmatisation, racist stereotyping) as they occur, but considers in depth and precision how the arcs of race, risk and security perpetuate this system. Secondly, on a practical level, a more cosmopolitan, comprehensive and inclusive deliberative democracy is required which can yield discernible change. Reforms in Catalonia and Oregon point to how this can be done, but also its precarity. Scaling it up and bringing in the voice of people who use drugs as part of a social movement is essential.
The text brings us almost full circle to how a better politics might lead to a more sophisticated, fairer form of market regulation.
Seddon points to the success of prison reform movements in France in the 1970s or the radical politics of mental health campaigning organisations which sought to foreground the voices of survivors of the psychiatric system as providing a blueprint. To this we could add decades of campaigning by disability rights activists, which have shown how positive change can occur with these strategies. There is no reason why drug policy should be any different. In this way, the text brings us almost full circle to how a better politics might lead to a more sophisticated, fairer form of market regulation. Ultimately, for Seddon, this means shifting the focus of social and political science away from the way the world is, towards the deeper thinking on the kind of world we want. This is the book’s challenge. It is us up to us to deliver.
Note: This interview gives the views of the author, and not the position of the LSE Review of Books blog, or of the London School of Economics and Political Science.
Image credit: OneSideProFoto on Shutterstock.
Building Socialism: The Afterlife of East German Architecture in Urban Vietnam – review
In Building Socialism: The Afterlife of East German Architecture in Urban Vietnam, Christina Schwenkel unpacks how the city of Vinh was reconstructed with the aid of East Germany in the aftermath of its bombing by the US between 1964 and 1973. Schwenkel skilfully combines historical analysis and ethnography to explore Vinh’s urban evolution, highlighting the challenges created through socialist planning and the enduring societal impact of Cold War urbanisation, writes Xue Xuan. This post was originally published on the LSE Southeast Asia Blog.
 In her book Building Socialism: The Afterlife of East German Architecture in Urban Vietnam, Christina Schwenkel tells of the neglected story of the Vietnamese city Vinh’s socialist reconstruction during the Cold War. This city was badly decimated by US air strikes between 1964 and 1973. To rescue Vinh from its ruins, East Germany provided substantial material and technological assistance that was designed to transform it into Vietnam’s model socialist city. However, this transformation was not without its challenges, as Vinh’s rapid ascendance was followed by a quick fall into “unplanned obsolescence”.
In her book Building Socialism: The Afterlife of East German Architecture in Urban Vietnam, Christina Schwenkel tells of the neglected story of the Vietnamese city Vinh’s socialist reconstruction during the Cold War. This city was badly decimated by US air strikes between 1964 and 1973. To rescue Vinh from its ruins, East Germany provided substantial material and technological assistance that was designed to transform it into Vietnam’s model socialist city. However, this transformation was not without its challenges, as Vinh’s rapid ascendance was followed by a quick fall into “unplanned obsolescence”.
Schwenkel skilfully weaves historical records with ethnographic research to dissect the architectural forms and planning practices of postwar Vinh, while also capturing its residents’ lived experiences within this changing urban landscape.
Schwenkel skilfully weaves historical records with ethnographic research to dissect the architectural forms and planning practices of postwar Vinh, while also capturing its residents’ lived experiences within this changing urban landscape. This historical ethnography of Vinh’s postwar reconstruction offers an in-depth exploration of state-led socialist modernisation, its vision, implementation and subsequent impact. During the Cold War, information about these urban experiments among socialist countries was largely inaccessible and unknown to the external world. To expose these facts contributes to a better understanding of socialist modernisation. It also resonates with the “multiplicity of experienced modernities”, thereby shifting the focus away from the dominant narrative of capitalist spatial production.
Schwenkel contends that socialist planning was both a “utopian science” and a “fantastical art of projection”, often venturing into realms of impracticality.
Interestingly, the book does not dedicate a specific section to explain what socialist urbanism is. Instead, its unique characteristics are gradually revealed across several chapters through detailed documentation of historical events and objects. Schwenkel contends that socialist planning was both a “utopian science” and a “fantastical art of projection”, often venturing into realms of impracticality. She examines two visual devices in the service of modernist planning: figurative drawing and abstract blueprints, delving deep into how these visual renderings of rationalised spaces sought to represent a universal socialist future. However, when materialised in buildings and infrastructures, the rational planning was far from fulfilling its promise: it neither increased labour productivity nor moulded enlightened proletarians. The author employs the case of Quang Trung Housing Estate to concretise how practical problems like poor material conditions and conflicting spatial practices inhibited the rapid construction of mass housing and how residents’ uncivil behaviours serves to contest quotidian forms of urban governance, epitomising the dialectical relationship between civilization and backwardness. The ethnographic approach of this study offers the author an opportunity to deliver a nuanced understanding of the lived experiences associated with socialist urbanisation. This perspective underlines the agency of citizens, challenging prevailing views that often portray citizens as passive participants. Schwenkel traces manifold ways that residents in Quang Trung made the decayed buildings adapt to their changing needs and urban lifestyles. Such acts, as demonstrated in the book, were not arbitrary but planned, which serves as individualised ways to pursue the unfinished utopia.
When recounting the destruction of Vinh during the war with the US, Schwenkel pays particular attention to the contrasting visual techniques employed by the US and Vietnam in reporting and recording urban warfare.
A particularly fascinating aspect of Schwenkel’s analysis is the focus on affect. She skilfully draws together socialist planning and its afterlife in mass housing through the thread of affect, generating many thought-provoking ideas. When recounting the destruction of Vinh during the war with the US, Schwenkel pays particular attention to the contrasting visual techniques employed by the US and Vietnam in reporting and recording urban warfare. In contrast with the aerial photographs by the US military, those photos taken by Vietnamese photographers employ close-up shots in recording the architectural remains of everyday urban life. The intimate portraits of the destroyed buildings powerfully convey the sense of trauma perceived by the people. This sense of trauma further strengthened international solidarity between East Germany and Vietnam, as detailed in the chapter “Solidarity”. It also set the stage for East Germany’s involvement in Vinh’s postwar reconstruction, which is thoroughly explored in the chapter “Spirited Internationalism”. This international solidarity, as demonstrated in the book, was both political and affective, appearing on the surface as a form of brotherhood between East Germany and Vietnam, but at its core, it was characterised by an asymmetrical relationship. The middle part of the book elaborates how this international solidarity gave birth to socialist planning and architectural forms in Vinh.
The author delves into the complexities of international solidarity as affective practice, highlighting the challenge of cultural differences, misaligned expectations, and the difficult balance between altruism and self-interest. The last part of the book features voices from the people of Vinh, who inhabited and used modernist architecture. Their affective attachments to the modernist architecture of the city are reflected in the various modifications they made to their residences, which subverts the narrow understanding of seeing modernist architecture as the product of rationality. To examine this state-sponsored, nationalist project through the thread of affect is very intriguing. It also piques my curiosity: how does affect relate specifically to socialist urbanisation as opposed to capitalist urbanisation? While the author briefly addresses this aspect in certain chapters, a detailed exploration is not provided.
The book not only sheds light on a lesser-known chapter of Cold War history but also propels readers to think about the lasting impact of architectural and urban planning decisions in shaping societal narratives and experiences.
The book’s strength lies in its methodological approach. Schwenkel’s transnational perspective, underpinned by extensive use of both German archives and Vietnamese sources, allows for a nuanced understanding of this complex historical interplay. By engaging with key informants in Vinh and delving into local archives, Schwenkel brings to the fore voices that have long been marginalised in historical discourse.
Building Socialism is a compelling read for scholars and enthusiasts of socialist urban planning and architecture, Asian urbanisation, and postcolonial studies. The book offers a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the socialist modernisation in the postwar city of Vinh. It not only sheds light on a lesser-known chapter of Cold War history but also propels readers to think about the lasting impact of architectural and urban planning decisions in shaping societal narratives and experiences.
This book review is published by the LSE Southeast Asia blog and LSE Review of Books blog as part of a collaborative series focusing on timely and important social science books from and about Southeast Asia.
This post gives the views of the author, and not the position of the LSE Review of Books blog, or of the London School of Economics and Political Science.
Image Credit: khuanchai photo on Shutterstock.
The Big Con: How the Consulting Industry Weakens Our Businesses, Infantilizes Our Governments, and Warps Our Economies – review
In The Big Con, Mariana Mazzucato and Rosie Collington claim that our overreliance on the consulting industry has negative consequences for society, inhibiting knowledge transfer and corporate and political accountability. The authors expose how consultancies’ goal of “creating value” may not align with addressing major issues such as climate change, arguing convincingly for greater transparency and a revitalised public sector, writes Ivan Radanović.
 In their book The Big Con, Mariana Mazzucato and Rosie Collington warn that relying on consultancies harms the public interest. Asking what happens to the brain of an organisation when it is not learning by doing because someone else is doing the doing, they conclude that societies must return public purpose in centre of attention.
In their book The Big Con, Mariana Mazzucato and Rosie Collington warn that relying on consultancies harms the public interest. Asking what happens to the brain of an organisation when it is not learning by doing because someone else is doing the doing, they conclude that societies must return public purpose in centre of attention.
The authors’ thesis is that overreliance on consultancies harms public interest, disables governments, and threatens democracy.
In 2021, the consulting industry was valued at over 900 billion dollars. Its ninefold rise since 1999 is the result of rising reliance of states on consulting agencies. The authors’ thesis is that overreliance on consultancies harms public interest, disables governments, and threatens democracy. They investigate this trend and how to reverse it.
The “Big Con” is the term Mazzucato and Collington use to mark the biggest auditing, accounting, and consulting agencies such as Ernst & Young (EY), KPMG, PwC, Deloitte, McKinsey, Boston Consulting Group (BCG), Accenture and others. The consulting market emerged during early industrialisation, when engineers, periodically recruited by major industrial firms, formalised their work. In the 1920s many consultants, among them James McKinsey, cooperated with American businesses. The popularity of management consultancy rose in 1970 when BCG introduced the matrix for mapping the profitability of business portfolio. After two years, this tool was used (and paid for) by more than 100 enterprises. American firms, on the wings of the Marshall plan and later IT management projects, have spread throughout Europe.
Golden years
The election of the right-wing populists Margaret Thatcher in the UK (1979) and Ronald Reagan in the US (1981) occurred after a decade of economic turmoil, led by the end of the Bretton Woods system and two major oil crises. The opinion that the responsibility for the turmoil lay in how states were run mushroomed. The neoliberal credo was that the only value creators in society are markets, and with Thatcher and Reagan, favour was refocused from the worker to the citizen-taxpayer.
The neoliberal credo was that the only value creators in society are markets, and with Thatcher and Reagan, favour was refocused from the worker to the citizen-taxpayer.
Contrary to the belief that the essence of neoliberalism is to slash public spending, Mazzucato and Collington suggest “it is more precise to describe it as public spending redirection towards the stronger role of the market” (49). In Thatcher’s era (1979-1990) government expenditure rose in real terms by 7.7 percent (43). In Reagan’s (1981-1989) federal spending rose by almost nine percent annually (43). From the US to Australia, thousands of neoliberal reforms such as privatisation, deregulation or outsourcing states had to be implemented, and advised. The authors show us that the annual public spending for consulting in the UK from 1979 to 1990 rose fortyfold – from 7.1 million to 290 million dollars. The 1980s saw the advent of a new management doctrine. In place of earlier stable forms of organisational life emerged the model of flexible “learning organisations” which view instability as an opportunity. The main goal becomes maximising value for shareholders. In the 1990s, that led to the popularisation of storytelling in politics and business. It is no longer a product or brand that is sold, but the story about value, challenges and business success through positive change, peddled by elite consultants or management gurus.
Creating the impression of value
Today, consultants are seen as experts who transfer know-how and utilise advanced management techniques to improve clients’ businesses. The enormous rise of consulting in the last four decades is explained by the “value” they create for states and companies. However, according to the authors, consultants do not always meet expectations and they seldom transfer knowledge. Created “value” is often unclear and depends on the perception of the client. Consultants hustle to create the impression of value.
Created “value” is often unclear and depends on the perception of the client. Consultants hustle to create the impression of value.
There are many examples where engaging consultancies has backfired for states. In developing countries such as Nigeria, Mexico and Angola, hiring consultancies was a condition of their IMF loan agreements (50). The authors focus on wealthy countries, arguing that even if contracting consultants experienced in the implementation of complex macroeconomic programmes could be justified in developing countries, it is less justifiable in developed countries, which should ostensibly have high competency in these areas.
Unmet deadlines, spiralling costs
Consultancies often fail to deliver on their promises. In 2010, Sweden started the construction project for a new university hospital in Stockholm which would be the most advanced in Europe. Its operations were to be grounded in “value-based healthcare”, a concept designed by management guru Michael Porter. Costs were initially valued at 1.4 billion euro, with the project set to be completed in 2015. City authorities opted for a public-private partnership which contracted consultants from PwC and EY who claimed they would ”maximise the value and keep the costs under control” (145). Representatives from the construction company Skanska stated that this model would “transfer the risk from the state and taxpayers to the private sector” (145). However, the costs immediately surpassed the projections because vital equipment had not been included in the budget The project, beset by problems, was passed to BCG, who had nine consultants working on its implementation while earning a monthly salary of almost 70,000 euros over six years. Another consultancy, Nordic Interim AB was then contracted for an additional 12 million euro, and when the hospital was eventually finished in 2018, costs a billion euros higher than the original estimate.
Absence of accountability
It is not all about money. Consultancies contribute to many undemocratic practices, maintaining what Acemoglu and Robinson named as extractive institutions. Often, they act as a mechanism for public wealth extraction, whereby states recruit consultants when they want to “hedge” the political risk of unpopular economic measures. The states maintain legitimacy, and consultants get their share of political influence. Authors emphasise the example of Puerto Rico, which faced bankruptcy in 2016. Then-President Obama initiated the creation of an Oversight Board to supervise the bankruptcy process. Keeping reputational risk low, Washington ensured that the majority of members of the Board were of Puerto Rican heritage. The Board did not hire a large staff, to avoid looking like it was setting up a parallel government. Instead, it brought in consultants. Instead of the state, McKinsey engaged in the privatisation of public enterprises, healthcare reforms “based on value”, slashing public spending and restructuring debt. Moreover, McKinsey owned $20 million of Puerto Rico’s bonds: consultants were set to profit from the very same debt they were helping to restructure.
Regaining control
Even though consultancies did not cause the maladies of neoliberal capitalism, they have profited from them. Without transparency and democratic permission, they erode the capabilities of states and enterprises. Because knowledge is not cultivated within state workforces and institutions, a dependency on the “expertise” of consultancies spirals.
[Consultancies] erode the capabilities of states and enterprises. Because knowledge is not cultivated within state workforces and institutions, a dependency on the “expertise” of consultancies spirals.
The last section of the book is about “climate consulting”. Omnipresent and long-term, climate change is ideal ground for consultants. Competition is fierce; consultancies’ “websites are replete with beautifully designed free reports on sustainability issues for every sector, from oil and gas to healthcare” (190). They promise solutions, pitching themselves as an avant-garde of change.
The key takeaway, according to Mazzucato and Collington, is that we must challenge the predominance of consultancies. With their ultimate goal of “creating value”, they advise both the fossil polluters and the governments mandated to reduce emissions. Moreover, states are catalysts of technological change for public good, while the private sector only invests in fundamental research when it becomes enticingly profitable.
Putting aside the authors’ techno-optimistic view – which holds that climate change mitigation is mostly a technical issue regarding innovations for green transition, which is being debunked – their final suggestions are valid. A new narrative and vision for the role of the state, recovering public capacities, embedding knowledge transfer into consulting contracts’ evaluation and mandating transparency are, undoubtedly, desirable. The book’s importance lies in how it reveals the political implications of the consulting industry. Whether we choose “green growth” or abandon the growth imperative, one thing is certain: democratically elected governments are key actors. Only they can mobilise the resources required for achieving “moonshot” missions, the most urgent of which is climate change.
Note: This interview gives the views of the author, and not the position of the LSE Review of Books blog, or of the London School of Economics and Political Science.
Image credit: Alena Veasey on Shutterstock.
Locked Out of Development: Insiders and Outsiders in Arab Capitalism – review
In Locked Out of Development: Insiders and Outsiders in Arab Capitalism, Steffen Hertog critiques mainstream development models in the Middle East, focusing on state intervention and segmented market economies. Although Yusuf Murteza suggests the book under-examines neoliberalism’s prevalence, he finds its analysis on the state’s role in establishing the insider-outsider division in the economy nuanced and valuable.
 Clusters of economic and political theorists have long been discussing how different actors prioritise and frame their understanding of “development”. Post-development and degrowth scholars such as Arturo Escobar, Gustavo Escobar, Wolfgang Sachs, and Jason Hickel announced the death of the mainstream development model as a project. They argued “the project of development” may not be equally beneficial to all societies, since the project carries ethnocentric and universalist dimensions which contribute to the hegemony of the West.
Clusters of economic and political theorists have long been discussing how different actors prioritise and frame their understanding of “development”. Post-development and degrowth scholars such as Arturo Escobar, Gustavo Escobar, Wolfgang Sachs, and Jason Hickel announced the death of the mainstream development model as a project. They argued “the project of development” may not be equally beneficial to all societies, since the project carries ethnocentric and universalist dimensions which contribute to the hegemony of the West.
The ‘one size fits all’ idea of neoliberal development, which utilises finance and corporate capital, has gradually been replaced by alternative forms of development
The “one size fits all” idea of neoliberal development, which utilises finance and corporate capital, has gradually been replaced by alternative forms of development. Growing disillusionment with the Anglo-Saxon economic model increased the importance of examining alternative political and economic configurations both inside and beyond developed Western states. Varieties of Capitalism (VoC) theory’s significance can be grasped with its emphasis on existing similarities and differences within the institutions of developed economies. Recently, scholars have taken these insights seriously and benefited from the VoC framework to explain the reasons why political and economic institutions differ across societies. Discourse on the MENA region in terms of democracy and development may suffer from orientalist explanations that directly link religion and culture to the region’s political and economic stagnation. Steffen Hertog’s Locked Out of Development takes issue with what mainstream development scholars consider the political and economic inability of societies in the Middle East to take the Western route and realise neoliberal reforms in order to ensure economic development, productivity and innovation.
Neoliberal narratives suffer from a partial outlook. They trace the failures of development attempts by focusing on policymakers’ level of adherence to marketisation and privatisation.
Hertog’s main arguments throughout the book are threefold. First, neoliberal narratives suffer from a partial outlook. They trace the failures of development attempts by focusing on policymakers’ level of adherence to marketisation and privatisation. They consider ensuring faith in the market mechanisms of production and distribution systems as paramount. However, non-economic, country-specific problems matter. In the case of the Arab world, the deep dividing line of insider-outsider segmentation across societies has more explanatory power than classical narratives of having too much or too little market (81). Second, Hertog believes a comparative perspective situated within a global context carries crucial insights. The selected countries cannot be examined solely by focusing on within-region differences but should be considered within the global development trajectory and compared with developed countries (7). Third, the role of the state has a somewhat ambiguous position in development theory. The concept of a “developmental state” has added a further twist. The characteristics of the state and its symbiotic relationship with labour and the private sector need to be addressed when explaining factors contributing to the persistence of the Arab world’s development problem (8).
The role of the state has a somewhat ambiguous position in development theory
Hertog begins with a detailed examination of academic literature on the political economy of the Middle East, the varieties of capitalism approaches, and his conceptualisation of segmented market economies (SEME). The second chapter adopts a historical perspective and presents the case selected countries’ political and economic transformations after World War II. In the third chapter, Hertog reveals his argumentation of the SEME framework by bringing the state, labour market, business sector and skill composition to light. Detailed analysis of the country case studies follows, accompanied by SEME and future research directions. Lastly, Hertog sums up the reasons for the political and economic inability of the region to take the Western route.
Hertog argues that the VoC approach, with its emphasis on the heterogeneity of existing capitalisms, is useful to explain the unique characteristics of Arab capitalism. Different compositions of firms, the finance sector, networks, and the skill system create ideal-type interactions (those which typify certain characteristics of a phenomena) and lead to diversification within capitalism. The original VoC approach analysed several OECD countries from the developed world. In time, scholars used the explanatory power of VoC to explain the development performances of non-Western countries with specific modifications. Taking insights from recent accounts of VoC literature, Hertog believes the approach fits the Arab world well (8).
In broad terms, the state [in the Arab world] functions as the voice of insiders’ interests to quash any outsider’s attempt to reconfigure access to key resources.
There are two key dynamics in the region. As the second chapter discusses, the state has been a key actor in structuring the playing field between different interests to operate in the region (9). The interventionist and distributive characteristics of the state go hand in hand with the other dynamic, namely the persistence of insider-outsider division in the economy. In broad terms, the state functions as the voice of insiders’ interests to quash any outsider’s attempt to reconfigure access to key resources. Hertog warns that the nuanced structure of the SEME model applies only to the core members of the region, such as Algeria, Egypt, Jordan, Morocco, Tunisia, Syria, and Yemen. The key filter behind this selection of countries is their state-building projects between 1950 and 1970 (4-5).
Strategies of keeping public sector employment high with military jobs, large redistribution policies, food subsidies, and price controls are still prevalent in the region, demonstrating its nationalist and statist legacy.
Hertog finds the roots of his SEME model in Arab nationalism in the post-independence era. The state-building projects of the selected countries fused with nationalist and statist ideologies at the time. Discussion on the region’s long history brings up the question of path-dependence, which is used to describe the limiting power of past decisions over later trajectories. Hertog avoids engaging with these long-term theories, believing them unsuitable for a short book, and the key characteristics of the SEME model originated recently. Nationalisation policies and active intervention in the economy were characteristics of Arab nationalism (15). In state-building projects, Egypt and Syria set the parameters, which were later copied by other states. Strategies of keeping public sector employment high with military jobs, large redistribution policies, food subsidies, and price controls are still prevalent in the region, demonstrating its nationalist and statist legacy (28).
The detailed empirical discussion of the SEME is at the heart of the book. The framework is constituted by the state, labour market, business sector and skill system (9). The distributive character of a state can be located by examining the share of public employment, which remains high from a global perspective. Also, the state extensively regulates labour markets, holding key strongholds to access land and credit (29-30). Hertog argues these factors lead to segmented labour and private sectors, while keeping the skill level low. The presence of the state in the labour market ensures insider-outside division. Since there is little mobility, insiders rarely lose their position. Outsiders cannot reach to the welfare protection schemes by the state. This leads to social exclusion and an unproductive environment (32-48).
Hertog claims state intervention in the private sector creates unique opportunities for crony networks, whereby politically connected companies benefit from credits and licences.
Similar dynamics take place in the business sector, where large firms and clusters of small firms coexist (55). Hertog claims state intervention in the private sector creates unique opportunities for crony networks, whereby politically connected companies benefit from credits and licences. Business actors with outsider status engage in unproductive small-scale activities (58-60). The skill system needs to be thought of in relation to the segmented labour and business sectors. Low skill levels prevent mobility and limit innovation and technological development (69).
Overall, Hertog argues that state intervention in the region establishes the insider-outsider division in the economy. Hertog’s emphasis on bringing the state back into the analysis is beneficial. In the field of comparative politics, the idea of the state as an autonomous actor remained on the margins until the 1980s. The book’s limitations come in two forms. First, it doesn’t mention how global capitalist relations fit into the SEME. Hertog’s defence with the limitation of economic globalisation in the region may not offer a solution, since the dynamics of global capitalist accumulation depend on drawing materials from peripheral countries without contributing to them. Second, Hertog’s claim of neoliberalism’s low presence in the Arab world is dubious. Several scholars (Jason Hickel, Philip Mirowski) argue that states with strong capacity can implement the necessary reforms for deregulation and privatisation. Thus, the presence of neoliberalism and strong state capacity is not mutually exclusive. In the Middle East, we see a unique mixture of neoliberal policy reforms with strong state capacity. Even though Hertog constructs his own case, adapting earlier approaches to VoC and development topics and to explain the MENA region, policymakers, development specialists, and academics will find dry economic analysis alone is not enough. More nuanced analyses that consider the symbiotic interactions between the state, the business sector, and labour force are necessary. Only by doing this is it possible to acknowledge how politics mingle with economics, and to design alternative development programmes in response.
This post gives the views of the author, and not the position of the LSE Review of Books blog, or of the London School of Economics and Political Science.
Image Credit: AlexAnton on Shutterstock.
Online Philosophy Resources Weekly Update
The weekly report on new and revised entries at online philosophy resources and new reviews of philosophy books…

Reminder: if your journal publishes open-access book reviews, please send in links to them for inclusion in future weekly updates.
New:
- Ruth Barcan Marcus by Roberta Ballarin.
- Bradley’s Moral Philosophy by Dina Babushkina and David Crossley.
Revised:
- Voluntary Euthanasia by Robert Young.
- Philosophy of Science in Latin America by Olimpia Lombardi, Alberto Cordero, and Ana Rosa Pérez Ransanz.
- Philosophy of Linguistics by Barbara C. Scholz, Francis Jeffry Pelletier, Geoffrey K. Pullum, and Ryan Nefdt.
- Japanese Zen Buddhist Philosophy by Shigenori Nagatomo.
- The Frege-Hilbert Controversy by Patricia Blanchette.
- Scientific Reduction by Raphael van Riel and Robert Van Gulick.
- Samuel Ibn Tibbon by James T. Robinson.
- Fictionalism by Matti Eklund.
- Zeno’s Paradoxes by Nick Huggett.
- Pythagoreanism by Carl Huffman.
- Quantum Computing by Michael Cuffaro and Amit Hagar.
- Provability Logic by Rineke (L.C.) Verbrugge.
- Natural Selection by Peter Gildenhuys.
IEP ∅
NDPR ∅
Open-Access Book Reviews in Academic Philosophy Journals ∅
Recent Philosophy Book Reviews in Non-Academic Media
- Catastrophe Ethics by Travis Rieder is reviewed by Andrew Stark at The Wall Street Journal.
- Who’s Afraid of Gender by Judith Butler is reviewed by Brock Colyar at The Drift.
- What Are Children For?: On Ambivalence and Choice by Anastasia Berg and Rachel Wiseman is reviewed at Kirkus Reviews.
- Limitarianism: The Case Against Extreme Wealth by Ingrid Robeyns is reviewed by David Rosen at The New York Journal of Books.
- Two translations of Tractatus Logico-Philosophicus by Ludwig Wittgenstein—one by Alexander Booth and the other by Michael Beaney—are reviewed by Jonathan Rée at Literary Review.
Compiled by Michael Glawson
BONUS: Demarcation
The post Online Philosophy Resources Weekly Update first appeared on Daily Nous.