idaho
Conservative Idaho: Poised to Resist Sprawl?
by Dave Rollo

Idaho’s Sawtooth Mountain Range. (USDA)
The USA, Canada, and other countries have long recognized sprawl as a vexing dimension of urban development. Especially challenging is the difficulty creating the public consensus needed for political and planning responses to the problem.
But growing numbers of residents today are expressing their distaste for sprawling approaches to development and are primed to resist it. Perhaps surprisingly, sprawl afflicts a U.S. state better known for its natural beauty and its potatoes: Idaho. Even more surprising, and hopeful, is the growing opposition to sprawl among the state’s citizens.
An Urban Malignancy
Sprawl, one of the chief products of the urban growth machine, entails a development and building pattern that is damaging to the environment and to a community’s quality of life.

The monotony of sprawl replaces farmland and natural habitat. (Mark Strozier, Flickr)
Characterized by an expansive diffusion of roads, housing, and other built infrastructure, sprawl has become ubiquitous across the USA and Canada. With its emphasis on separation of commercial, residential, and public uses, sprawl employs great quantities of concrete and asphalt infrastructure and promotes car use. Furthermore, its high energy demands are maladaptive for a future of energy limits. Lax and aesthetically unimaginative design standards create a monotonous landscape that swaps traditional beauty for strip malls, big box stores, and McMansions.
Sprawl eats up natural habitats, demands huge amounts of resources and energy, and leads to isolation, social segregation, and other societal harms. However, in the short term, sprawl generates profits for development interests, especially when demand is high, and when planning codes permit or even encourage it.
Losing Natural Assets
Idaho is ecologically rich and abundant in quality farmland, rangeland, and water resources, assets threatened by pro-growth development in cities and counties across the state.
Idaho is often ranked in the top tier of states endowed with natural beauty. It borders Yellowstone National Park and the Grand Tetons and includes the strikingly beautiful Sawtooth Mountain Range, which runs through the center of the state. That range boasts four unique plant and animal communities and provides habitat for numerous species. Idaho’s natural features also include sagebrush steppe, an ecosystem that supports 350 rare, threatened, and endangered species.
Besides its magnificent wildlands, Idaho is endowed with a vibrant agricultural base, composed of some 25,000 ranches and farms. Food abundance is evidenced by the state’s seventh-place ranking in the USA for agricultural exports per capita. Furthermore, 26 percent of Idaho’s agricultural land is considered “nationally significant” by the American Farmland Trust; that is, it ranks among the best in the nation for long-term food production.
Yet Idaho’s natural assets are threatened by population pressure, which often drives land conversion. Idaho is one of the two fastest-growing states, with immigration from California accounting for nearly 40 percent of Idaho’s population increase in 2021. Spokane Public Radio reports that Idaho is projected to add 800,000 residents by 2060, an increase of 42 percent from the current population.
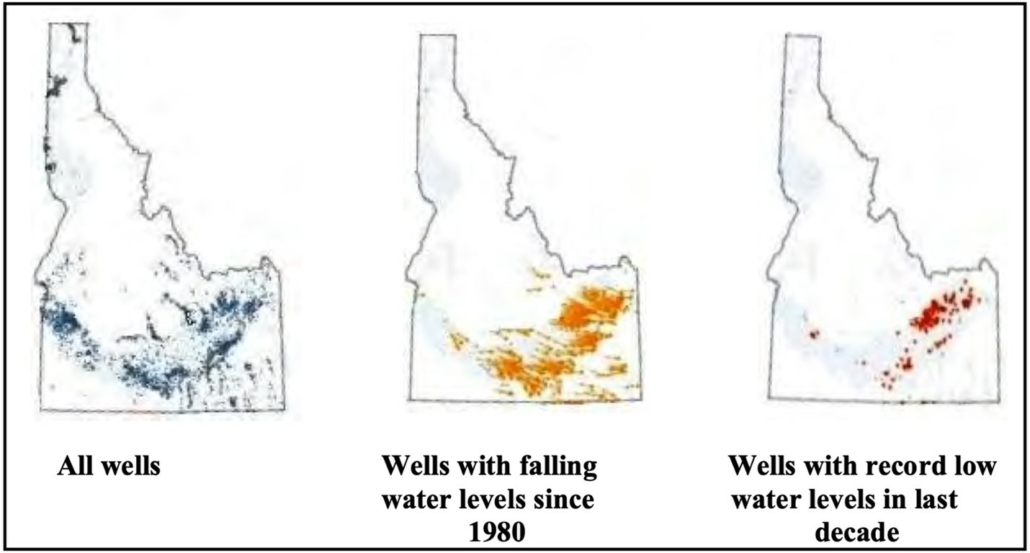
Aquifer depletion is already a problem in Idaho. (NumbersUSA)
This population pressure was largely responsible for the loss of some 370,000 acres of farmland and natural habitat between 1982 and 2017. The nationally significant share of agricultural land was more than three times as likely to be developed as other cropland. Population increase and attendant sprawl negatively impacts the sagebrush steppe in Idaho, with the greatest decline in ecological integrity in the fastest-growing regions of the state.
Apart from displacing cropland and wildlife habitats, new residences place added pressure on water tables, which are falling in Idaho. As aquifers trend toward depletion, allocating more water for a growing population will only serve to exacerbate the problem—in part through arguably wasteful uses of water, such as irrigation of turfgrass lawns, which competes with agricultural irrigation. Increased economic activity also generates contaminated stormwater, septic leakage, and yard pesticides that seep into groundwater and adversely affect aquifers.
Gauging Sentiment and Building Consensus
Prospective increases in the human population and the evident failure of land use regulations to limit the impact of growth have alarmed many residents of Idaho. Concerns about farmland loss and the degradation of Idaho’s environment prompted a 2023 study to assess the problem of population growth and sprawl in Idaho and take the pulse of the populace.
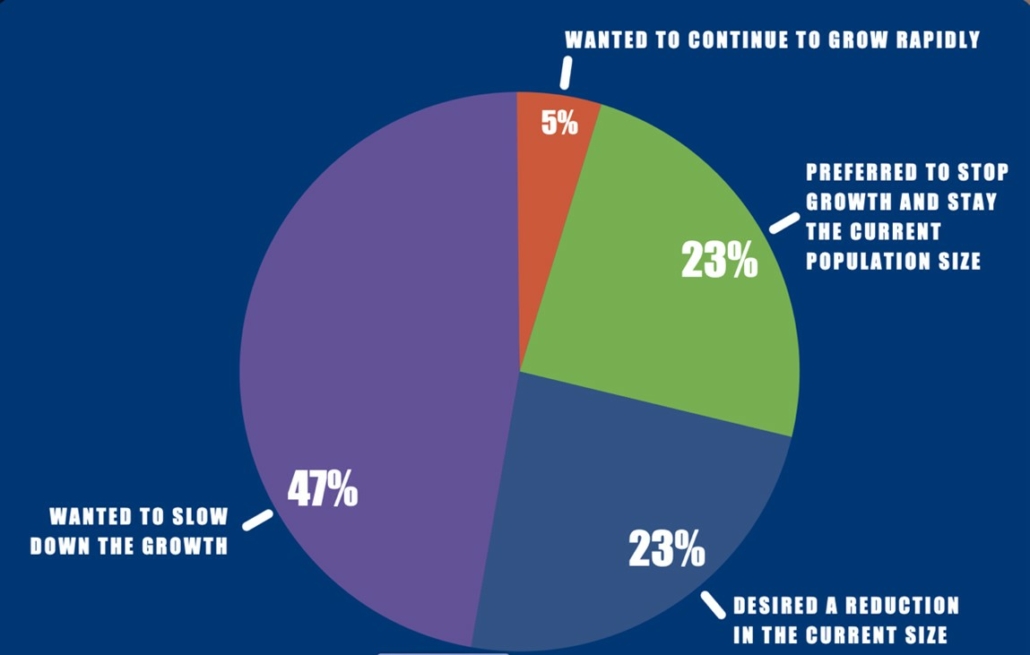
The overwhelming majority of Idaho residents see population growth as a problem. (www.IdahoSprawl.com).
NumbersUSA, a non-partisan, non-profit organization that advocates for “sensible immigration reform,” published a report on the study last month. The report establishes in detail the degree of habitat and farmland loss over several decades. Of the 370,000 acres lost, 77 percent was due to population increase, while 23 percent was caused by land conversion by the existing population.
The report also contains a survey of Idaho residents conducted by Rasmussen Reports that documents public awareness of sprawl and concern over it. More than three-quarters of respondents believe Idaho’s growing population negatively affects its open spaces and environment. And fully 93 percent see current growth as a problem and wish to slow, reverse, or stop it.
Furthermore, aquifer depletion is on the public’s mind. Some 73 percent of respondents oppose diverting water from agriculture to development. Clearly the citizens of Idaho understand that it’s not in their interest to compromise a precious and limited resource.
Addressing the Problem
Besides assessing the contextual problem of sprawl in Idaho, the report addresses how urban areas could implement zoning code changes to restrict encroachment of development, thus protecting farmland and natural features such as forests or sagebrush steppe.
Permissive land use (zoning) codes are one way sprawl is unleashed. Sprawl is also promoted when developers are not required to internalize the costs of added community infrastructure, such as water and sewer lines. Their development activity is essentially subsidized by taxpayers.
Various zoning tools can mitigate the impact of sprawl by incentivizing density. Tools such as the transfer of development rights, infill strategies, and permitting multifamily apartments instead of single-family housing all help to limit diffused development patterns. Implemented appropriately, these tools can increase density in ways that increase overall livability.
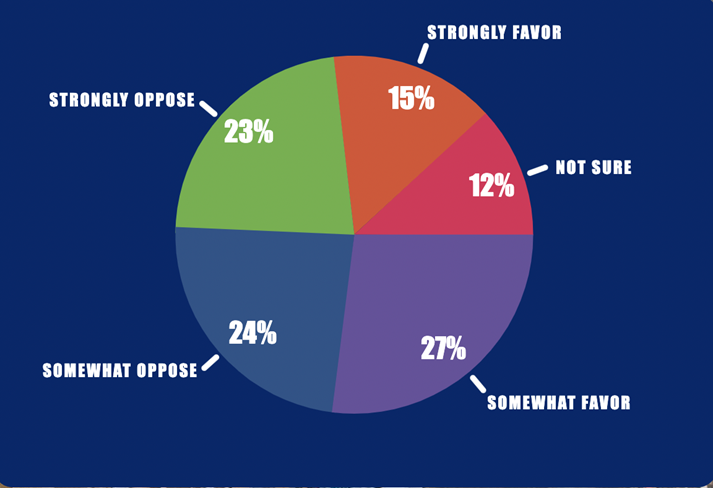
Sentiments of Idahoans on zoning that encourages high-density development. (www.IdahoSprawl.com).
The NumbersUSA poll indicates that Idahoans are split on this approach, with 42 percent favoring regulations that encourage apartments and condos over single-family housing versus 47 percent strongly or somewhat opposed to such regulations.
While the approach of internalizing costs—that is, increasing development fees to offset the costs to the community for new development—was not directly addressed by the poll, Idahoans are resoundingly opposed to public subsidization of new development. Nearly 80 percent of respondents expressed opposition to paying higher property taxes to cover the infrastructure costs of new subdivisions.
Pressure on public infrastructure such as roads, sewers, water utilities, police and fire stations, and schools increases with an expanding population and its growing economy, and these facilities often become overextended. The costs of such services are supposed to be borne by the new residents, but are externalized to the existing residents.
One way to prevent such externalization is to impose caps on services. For example, sewer hook-ups can be limited. Limiting hook-ups to sewage lines and wastewater treatment plants was favored by half of respondents, while 22 percent were unsure and just over a quarter were opposed.
Up to the Challenge?
While it’s clear that population growth and the development pressures that follow are negatively affecting residents of Idaho, their county and municipal governments are having a limited impact in restraining sprawl as planners continue with a business-as-usual approach to development.
Recognizing sprawl as a threat should be made explicit within county planning documents and clear measures to limit sprawl should be specified. Yet, the comprehensive plans of seven of the eight fastest growing counties in Idaho mention ‘grow’, ‘growth,’ or ‘growing’ 1063 times in all, while sprawl garners only 15 mentions. And most of the references to growth focus on how to accommodate it; little mention is made of growth’s negative impacts.

Greater density can mean greater livability (La Citta Vita, Wikimedia Commons)
Boise is Idaho’s largest city and its capital. It was also one of the first communities in the state to experience the impacts of sprawl. Sprawl from Boise continues at a fierce pace with 24,000 new residents pouring into the city in just the past 2 years. “Blueprint Boise” is the 2021 updated comprehensive plan for Boise, whose more than half a million residents comprise over a quarter of the population of Idaho.
While Blueprint Boise is similarly light on references to sprawl (a single mention), it offers some measures to mitigate sprawl. In response to population pressures, the comprehensive plan adopted strategies to add density and to guide growth within a set of neighborhood and area master plans.
But critics of the plan complain that it does not adequately describe the consequences of growth and sprawl. And they blame continued loss of farmland and other open spaces on the failure of regional coordination, especially the absence of concurrency. Concurrency is a planning concept that mandates that adequate public facilities be in place before development is approved.
The threats to Idaho’s natural places, farmland, and rangeland will continue as population and economic pressures mount. Most of Idaho’s counties are ill-equipped to address the pressures that come with the surge in population. Recent efforts to make clear to Idaho’s elected officials that action is needed are also bound to intensify. Bold action is required soon. Which communities in Idaho will choose to lead on confronting the problem of sprawl, inspiring others to follow?
Dave Rollo is a Policy Specialist at CASSE.

The post Conservative Idaho: Poised to Resist Sprawl? appeared first on Center for the Advancement of the Steady State Economy.